In an era defined by data proliferation and the imperative for precise communication, the ability to distil complex information into an easily digestible format is paramount. A well-constructed systematic review flow chart template serves as an indispensable tool for researchers, analysts, and project managers alike, providing a standardized framework for visualizing intricate processes, decision paths, and information flows. This template aids in documenting every stage of a systematic review, from initial search to final inclusion, ensuring rigor and transparency in methodology for all stakeholders involved in critical analysis and decision-making.
This highly structured document extends its utility far beyond academic systematic reviews, offering a robust foundation for any process requiring sequential steps, conditional logic, and clear outcomes. The template provides a coherent visual narrative, enabling users to rapidly grasp the progression of data points, project milestones, or even strategic initiatives. Its inherent organizational power benefits anyone responsible for presenting complex procedures with clarity and precision, from corporate strategists outlining market entry plans to public health officials detailing policy implementation.
The Importance of Visual Organization and Professional Data Presentation
Effective data presentation transcends mere aesthetics; it is a critical component of successful information exchange and analytical insight. Visual organization, particularly through structured flowcharts, enhances comprehension by leveraging the brain’s natural ability to process graphical information more efficiently than raw text. This method minimizes cognitive load, allowing recipients to quickly identify key relationships, bottlenecks, and dependencies within a system.
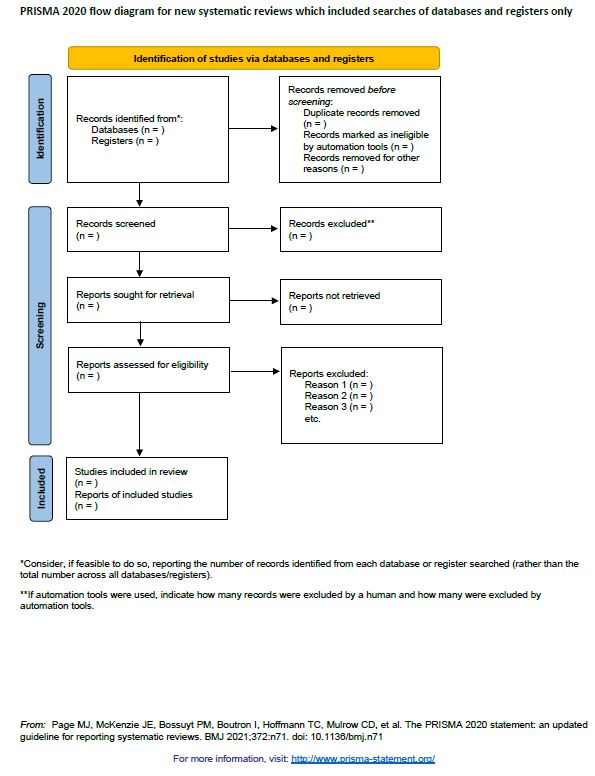
Professional data presentation underscores credibility and fosters trust in the information being conveyed. When data is presented clearly, consistently, and without ambiguity, it reinforces the author’s expertise and attention to detail. A well-designed infographic layout or chart design transforms raw numbers and procedural steps into actionable intelligence, empowering better-informed decisions across all organizational levels. It ensures that complex narratives are not only understood but also trusted as accurate representations of reality.
Key Benefits of Using Structured Templates, Visuals, or Layouts for Chart Creation and Presentation
Adopting structured templates for chart creation offers a multitude of strategic advantages for any organization. Primarily, it establishes a uniform standard for data visualization, ensuring consistency across various reports and presentations. This consistency is crucial for branding and maintaining a professional image in all internal and external communications.
Furthermore, using predefined layouts significantly reduces the time and effort involved in creating new charts from scratch. Analysts and project teams can focus on the content and insights rather than the intricate design elements, leading to increased productivity. These structured visuals also minimize the potential for errors, as the framework guides users through the necessary data points and logical connections, improving overall data accuracy and reliability.
Such templates also facilitate improved collaborative efforts. When all team members utilize the same chart design and presentation template, it streamlines communication, making it easier to share, review, and integrate information. This common visual language supports a more cohesive and efficient workflow, fostering a shared understanding of project status and analytical findings. The result is a more robust, data-driven decision-making process rooted in clear and consistent visuals.
How This Template Can Be Adapted for Various Purposes
The inherent flexibility of a systematic review flow chart template makes it remarkably adaptable across diverse sectors and applications. While its origins lie in academic rigor, its structural logic applies universally to any process that requires sequential steps, conditional branches, and clear endpoints. This adaptability makes it an invaluable asset for organizations seeking to standardize and clarify their operational procedures.
For business reports, this template can be reconfigured to illustrate market entry strategies, supply chain logistics, or customer journey mapping. It provides a visual roadmap for complex operational plans, helping stakeholders understand each phase and potential decision point. Similarly, for performance tracking, it can outline the stages of a project lifecycle, from initiation to closure, allowing teams to monitor progress and identify potential delays or resource reallocations effectively.
In academic projects, beyond systematic reviews, the chart can depict experimental protocols, thesis development phases, or the methodology of complex qualitative studies. For financial analysis, the visual can represent investment decision trees or the progression of an auditing process, enhancing transparency and clarity. Its core strength lies in its ability to translate intricate sequences into an intuitive, visually comprehensible format, suitable for diverse analytical and communication needs.
Examples of When Using a Systematic Review Flow Chart Template Is Most Effective
The application of a systematic review flow chart template proves particularly beneficial in scenarios demanding high levels of detail, clarity, and methodological consistency. Its structured nature ensures that no critical step is overlooked, and all conditional pathways are clearly articulated, fostering robust analysis and communication.
- Research Synthesis: Ideal for outlining the entire process of a literature review, from defining research questions and search strategies to screening articles, extracting data, and synthesizing findings.
- Regulatory Compliance Procedures: Effective for mapping out complex compliance workflows, detailing each step required to meet legal or industry standards, including decision points for approvals or rejections.
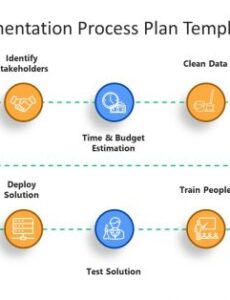
- Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC): Can be used to visualize the stages of software development, including requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance, with clear hand-offs between teams.
- Onboarding and Training Programs: Excellent for creating a visual guide for new employees, illustrating the step-by-step process for integration into a company, including required training modules and certifications.
- Customer Service Protocols: Useful for charting customer complaint resolution pathways, detailing initial contact, escalation procedures, potential solutions, and follow-up actions.
- Project Management Workflows: Applicable for mapping out complex project timelines, task dependencies, resource allocation processes, and critical path analysis, ensuring all team members understand their roles and responsibilities.
Tips for Better Design, Formatting, and Usability
Creating an effective flow chart goes beyond merely charting steps; it involves thoughtful design and careful formatting to maximize usability and comprehension. A well-designed chart enhances its practical value, whether presented in print or digital format. Start with a clear objective: what specific process or decision flow should this visual convey? This clarity will guide all subsequent design choices.
For optimal readability, employ a consistent color palette that differentiates elements without being distracting. Use a limited set of professional fonts, ensuring legibility at various scales. The use of shapes (e.g., rectangles for processes, diamonds for decisions) should also be consistent, following established flowchart conventions. Arrows indicating direction of flow must be unambiguous, avoiding confusing overlaps or ambiguous connections.
When considering report formatting, ensure that the chart integrates seamlessly with accompanying text. In digital versions, interactivity can enhance usability; clickable nodes that expand to reveal more detail or links to external documents are valuable additions. For print, ensure high-resolution graphics and sufficient white space to prevent a cluttered appearance. Always test the visual with an unfamiliar audience to gauge its clarity and effectiveness. Focus on minimizing visual clutter and prioritizing the flow of information; every element should serve a purpose in guiding the viewer through the narrative of the data tracking or process.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a visual that is both aesthetically pleasing and highly functional, transforming complex information into an accessible and actionable tool. Adhering to best practices in chart design and presentation template construction ensures that the intended message is conveyed accurately and efficiently. This commitment to detail in data visualization and infographic layout significantly amplifies the impact of any process documentation or analytical report.
The continuous evolution of data presentation methodologies underscores the enduring value of structured visualization tools. A meticulously crafted flow chart offers more than just a sequence of steps; it provides a comprehensive narrative that aids in understanding, analysis, and strategic planning. It transforms abstract processes into tangible, easily interpretable diagrams, ensuring that all stakeholders share a common operational perspective.
By serving as a consistent, adaptable, and visually effective communication instrument, this robust visual tool significantly enhances the efficiency of information dissemination and decision-making. Its practical utility in standardizing complex procedures, improving data accuracy, and fostering collaborative understanding makes it an indispensable asset in modern professional environments. Embracing such a data-driven and visually coherent approach is fundamental to achieving operational excellence and fostering clear communication in any endeavor.