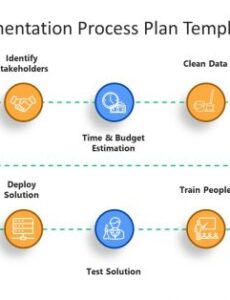
The efficient management of organizational processes is a cornerstone of operational success and strategic advantage. In contemporary business environments, clarity in communication and precision in documentation are paramount for maintaining productivity and fostering innovation. A robust work process flow chart template provides an invaluable framework for visualizing complex sequences of tasks, decisions, and outcomes, thereby enabling stakeholders to rapidly comprehend operational dynamics. This structured approach facilitates a transparent overview of workflows, from initial input to final delivery, ensuring every team member understands their role and the interdependencies within the system.
Utilizing such a template offers significant benefits by standardizing the representation of operational procedures. This form transforms abstract concepts into tangible visual representations, reducing ambiguities and enhancing collective understanding across departments. It serves as a foundational tool for internal documentation, training manuals, and compliance records, providing a consistent methodology for depicting intricate processes. The inherent structure of the template guides users through the systematic mapping of activities, conditional pathways, and critical milestones, fostering a more disciplined approach to process design and analysis.
The Importance of Visual Organization and Professional Data Presentation
In an era defined by information overload, the ability to organize and present data visually is no longer merely a preference but a strategic imperative. Visual organization dramatically improves comprehension by leveraging the human brain’s capacity for pattern recognition and spatial reasoning. Professional data presentation, particularly through structured diagrams, ensures that complex information is conveyed with maximum clarity and minimal misinterpretation, which is critical for effective decision-making. High-quality data visualization transforms raw data into actionable insights.
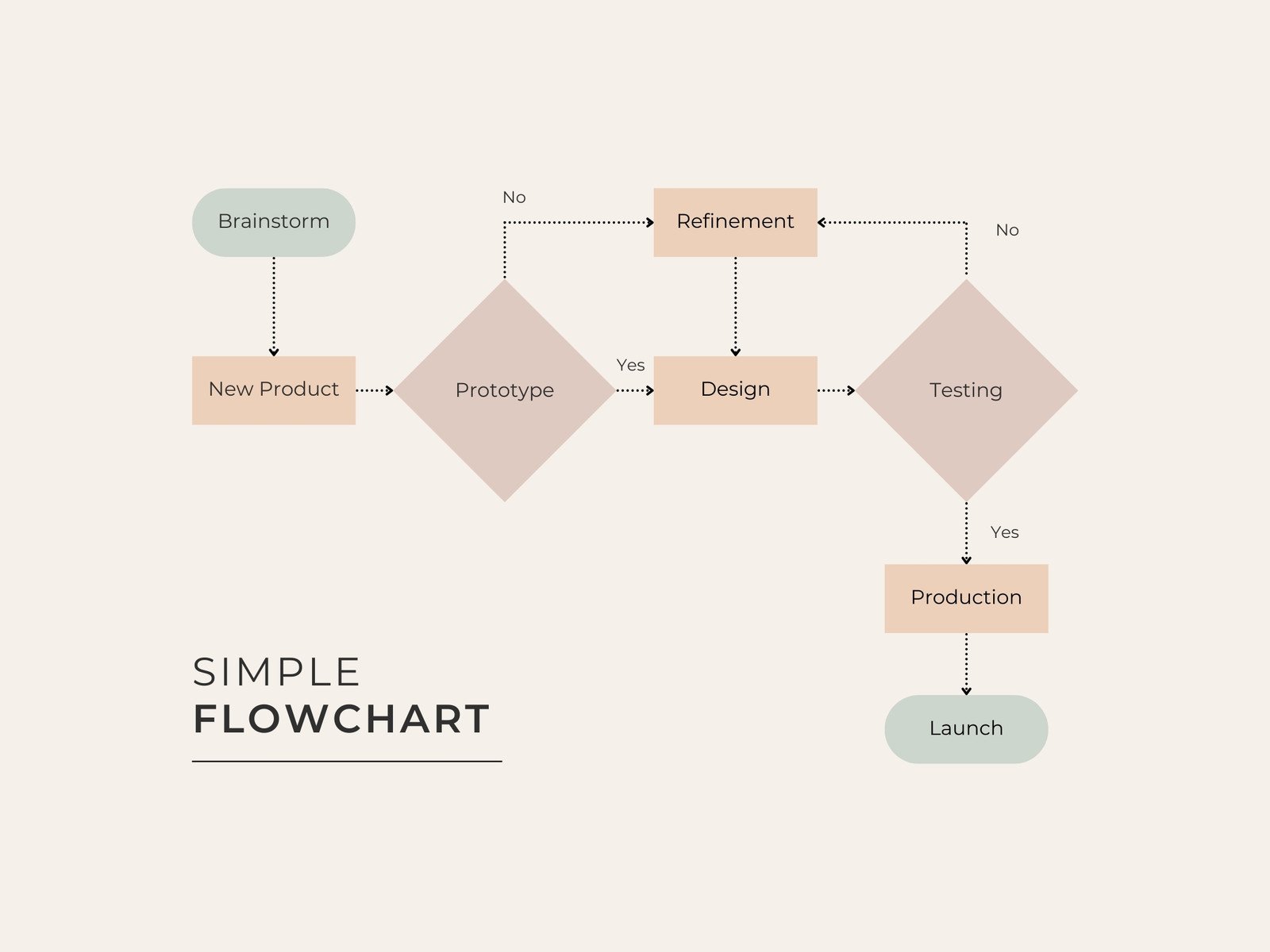
A professionally designed template facilitates the creation of a coherent narrative around process execution. It enables stakeholders to quickly identify bottlenecks, redundancies, or areas ripe for optimization, which might otherwise remain obscured within textual descriptions. The clarity afforded by a well-structured chart significantly reduces the cognitive load on the audience, allowing them to focus on the content’s implications rather than struggling with its interpretation. This emphasis on visual precision is essential for effective communication within and between organizations.
Key Benefits of Using Structured Templates for Chart Creation
The adoption of structured templates for creating process flow charts yields a multitude of operational and strategic advantages. These pre-designed layouts provide a consistent framework, significantly reducing the time and effort required to develop comprehensive diagrams from scratch. They promote uniformity in documentation, ensuring that all charts produced adhere to established organizational standards for aesthetics and content. This consistency is vital for maintaining professional presentation across all internal and external communications.
Structured templates streamline the entire data visualization process. They often incorporate standardized symbols and connectors, simplifying the depiction of various process elements such as starting points, decision nodes, and termination points. This standardization minimizes errors and enhances the readability of the resulting charts, making them accessible to a wider audience, regardless of their familiarity with specific processes. Furthermore, the use of a predefined layout encourages a systematic approach to process mapping, leading to more thorough and accurate representations. The template acts as a guide, ensuring all critical aspects of a process are considered and documented.
Adaptability for Various Business Purposes
The versatility of a well-designed work process flow chart template extends across a broad spectrum of organizational applications, making it an indispensable tool for diverse functional areas. Its inherent flexibility allows for seamless integration into various reporting and analytical contexts, demonstrating its utility beyond simple process mapping. For instance, in strategic planning, the template can illustrate the sequential steps for market entry or product development, mapping out dependencies and potential risks.
In marketing and sales, the visual aids can depict customer journey maps, from initial lead generation through conversion and post-sales support, highlighting touchpoints and communication flows. Human resources departments utilize such diagrams to outline recruitment processes, onboarding procedures, or performance review cycles, ensuring fairness and consistency. Finance teams can employ them to document expenditure approval processes, budget allocation workflows, or audit trails, enhancing transparency and accountability. The adaptability of the visual layout means it can effectively communicate intricate operational details for any department.
Examples of When Using a Work Process Flow Chart Template is Most Effective
Employing a structured template becomes particularly effective in scenarios where clarity, standardization, and collaborative understanding are paramount. Its utility shines in situations demanding a precise visual representation of operational sequences and decision points.
- Onboarding New Employees: Clearly illustrates the step-by-step process, from initial offer acceptance to first-week tasks, ensuring a smooth transition and rapid integration into the team.
- Software Development Lifecycle: Maps out each phase, including requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and deployment, clarifying roles and handoffs between development teams.
- Customer Service Call Flows: Details the progression of a customer inquiry, showing decision points for issue escalation, solution provision, or internal department transfers.
- Manufacturing Assembly Lines: Visualizes the sequence of operations, material flow, quality control checks, and potential rework loops, optimizing production efficiency.
- Project Management Phases: Breaks down complex projects into manageable stages, tasks, and milestones, aiding in scheduling, resource allocation, and progress tracking.
- IT Incident Response: Outlines the protocol for identifying, assessing, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security incidents, ensuring rapid and coordinated action.
- Financial Audit Procedures: Charts the systematic steps involved in examining financial records, from data collection to report generation, ensuring regulatory compliance.
Tips for Better Design, Formatting, and Usability
To maximize the impact and utility of any process flow chart, meticulous attention to design, formatting, and usability is crucial. A well-designed chart not only conveys information effectively but also enhances the professional image of the communication. For both print and digital versions, clarity and aesthetic appeal contribute significantly to overall effectiveness.
- Maintain Consistent Symbolism: Utilize a standardized set of shapes and arrows, such as those from BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) or basic flowchart symbols, for process steps, decisions, start/end points, and data. This consistency minimizes cognitive effort for interpretation.
- Strategic Use of Color: Employ a limited palette to differentiate process types, departments, or critical paths. Avoid excessive or clashing colors, as they can detract from readability. Subtle color coding can highlight specific elements like a performance dashboard or critical trend analysis.
- Clear Labeling and Text: Ensure all text within the diagram is concise, legible, and appropriately sized. Labels should clearly describe each step or decision without ambiguity. Use a professional, sans-serif font for optimal readability in both print and digital formats.
- Logical Flow Direction: Design charts to flow predominantly from left to right or top to bottom, adhering to conventional reading patterns. This natural progression simplifies understanding and navigation through complex processes.
- Optimal Layout and Spacing: Arrange elements with adequate spacing to prevent clutter. Group related steps logically and use swimlanes or functional areas to delineate responsibilities across departments, enhancing overall infographic layout.
- Version Control and Documentation: For digital charts, implement robust version control to track changes and revisions. For both formats, include a legend, creation date, and author information to ensure proper context and data tracking.
- Accessibility Considerations: Ensure digital charts are accessible, incorporating alternative text for images and ensuring color contrasts meet accessibility standards. For print, use sufficiently large font sizes and clear line weights.
- Iterative Review: Before finalization, solicit feedback from relevant stakeholders to identify potential inaccuracies, ambiguities, or areas for improvement in the chart design. This collaborative review ensures the diagram accurately reflects the real-world process.
By adhering to these design principles, the visual output becomes an intuitive and powerful communication tool. The intentional effort in creating clear, well-formatted charts pays dividends in enhanced comprehension and operational efficiency, regardless of whether it’s a simple bar graph or a complex series of interconnected operations.
Effective process documentation is a cornerstone of organizational excellence, fostering clarity, efficiency, and a shared understanding of operational procedures. The consistent application of a structured template for visualizing workflows offers a systematic approach to detailing complex sequences of tasks and decisions. This structured diagram not only standardizes communication but also serves as an invaluable reference for training, process improvement initiatives, and strategic planning across various departments.
Ultimately, the utility of a well-executed process flow chart extends beyond mere documentation; it acts as a dynamic tool for performance tracking and continuous optimization. By providing a clear, visual representation of operations, the template facilitates rapid identification of inefficiencies and opportunities for enhancement. Leveraging this visual communication record empowers organizations to maintain agility, ensure operational transparency, and drive continuous improvement, solidifying its role as an indispensable asset in any professional setting.